How to Fix Error While Copying in Ubuntu?

Are you trying to copy or move files within the Ubuntu File System but constantly encountering errors? If that is the case, this guide has been crafted for you!
File management is an important aspect when working in any Operating System. However, this is especially true within the Ubuntu File System, even though you are a normal user or a System Administrator.
Ubuntu System (especially Ubuntu Servers) can be daunting when managing files within its File System, and you can encounter errors of various kinds. Each error that occurs during the copying of files has a specific reason and a specific solution. This guide will explain the errors and solutions you can encounter when copying files in Ubuntu.
Table of Contents
Let’s get started!
How to Fix Error While Copying in Ubuntu?
If you are working on a Ubuntu System with a GUI available, you can try using the GUI drag-and-drop or the copy options in the right-click menu. Otherwise, you can use the “sudo” keyword at the start of the command if you are met with a permission denied error while trying to copy files in Ubuntu.
Moreover, if you encounter the error that the “file is too large” when trying to copy into an external drive or a USB Stick, you have to change the Format of the external storage drive to NTFS.
Let’s have a deeper dive into these errors and their solutions!
Use the “sudo” Command
You can encounter a “permission denied” error when copying a file into a directory without having adequate permissions for either the file or the destination directory. A quick and simple fix for this error is to use the keyword “sudo” at the beginning of the copy (cp) command.
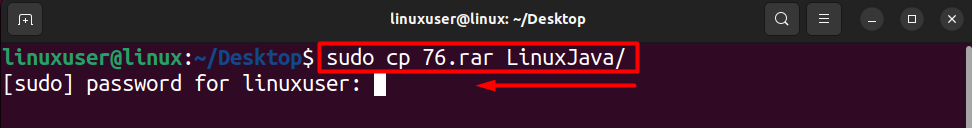
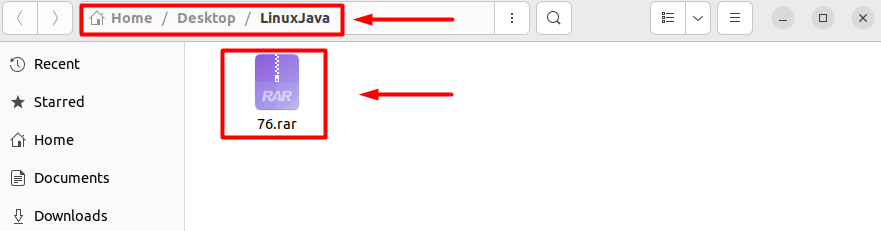
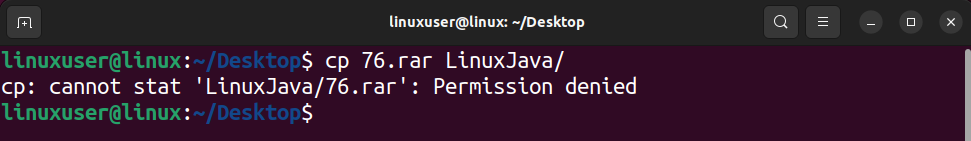
To demonstrate this using an example, assume you want to copy the file 76.rar into the folder “LinuxJava” placed on the Desktop, as shown in the image below.
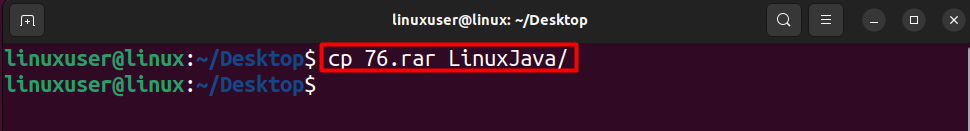
Normally, the command to perform this task is as follows.
cp 76.rar LinuxJava/
However, with the addition of the sudo keyword, the command changes to.
sudo cp 76.rar LinuxJava/
Keep in mind when you execute this new command, you will require the password for the root user to be able to perform the copy. Therefore, when prompted about the password, type it in and press the “Enter” key.
This method allows you to copy the files from one location to another without encountering the permission denied error. Afterward, you can verify the copy action by opening the destination directory.
Switch to Sudo(root) Shell
Another way of dealing with the permission denied error while copying files from one location to another is to shift over to the root shell. This removes the need to type the “sudo” keyword with every copy command you want to execute, making it a time-saving method.
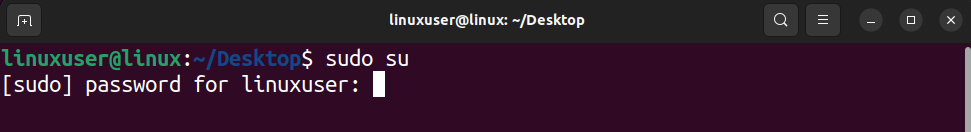
To shift over to the sudo shell, open up a new terminal in your Ubuntu system and type the following command inside it.
sudo su
Like the previous method, executing this command will require you to provide the root user with the password.
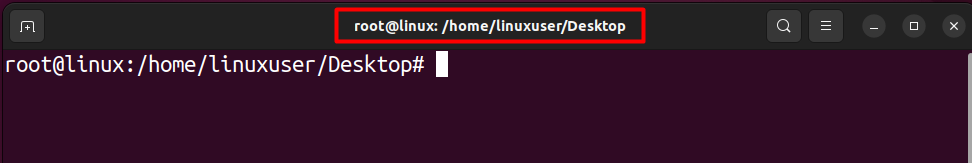
Once you have typed in the password for the sudo user, press the “Enter” key to execute the command. Afterward, you will see that the terminal has been switched with a root shell.
Afterward, you must run the copy command (cp), and the file will be copied to the destination directory without permission denied error.
However, be careful when inside the root shell, as all commands will execute with the highest authority, which means any wrong command can damage or remove the system files without any prompts.
Affordable VPS Hosting With Dracula Servers
Looking for reliable and budget-friendly Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting? Look no further than Dracula Servers. Dracula Servers offers a range of VPS hosting plans tailored to meet diverse needs. With competitive pricing, robust performance, and a user-friendly interface, it’s an excellent choice for individuals and businesses alike.
Explore the Dracula Servers website to discover hosting solutions that align with your requirements and take your online presence to new heights with their affordable and efficient VPS hosting services.
Visit Dracula Servers and experience reliable VPS hosting without breaking the bank.
Fix Read-Only Directory Error
If you try to copy a file into a directory with read-only access permission, you will encounter an error. This “permission denied” error can be fixed by using the previous method, but running commands with sudo privileges all the time is not a good practice.
To demonstrate this, assume you want to copy the file “76.rar” into the directory “LinuxJava” which has read-only permissions. Running the copy (cp) command will give you the following error statement.
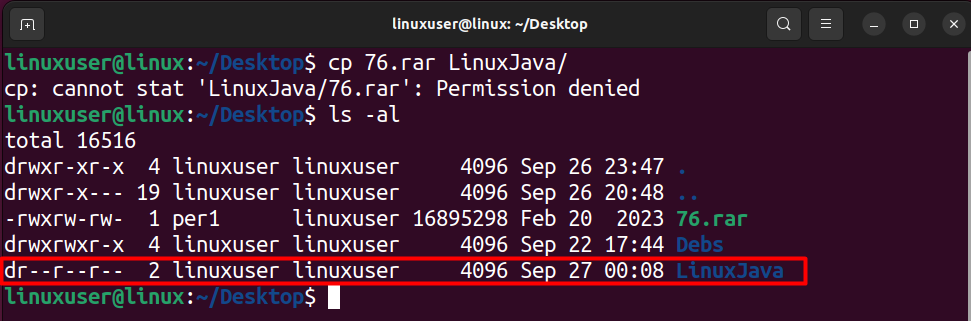
To resolve this error, confirm the permissions of the destination directory by running the following command in the terminal.
ls -al
You can observe from the image above that the permissions are set as “read” for all users. To change this access right, run the following command.
sudo chmod 550 LinuxJava/
You will type the directory name in which you want to copy the files. Once that is done, re-run the copy command, which will complete without encountering any error.
Correct File Format For External Storage Devices
You can encounter the “Files too large” error when copying files into an external storage drive, even when you have adequate space in the external drive. The main reason for this error is the incorrect format type of the External storage drive. If your pen drive or any other external storage device has a format of “FAT32” or “msdos,” then file operation bigger than 4 GBs is not allowed.
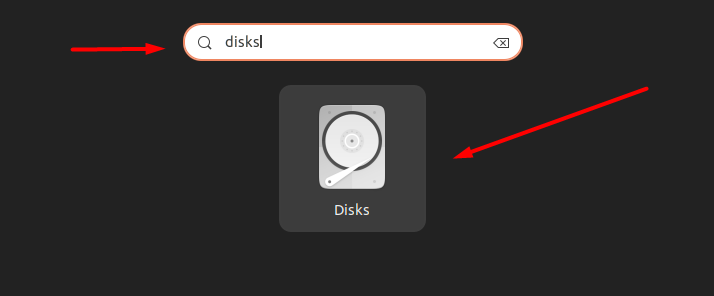
To fix this issue, click on the application icon from the left-side navigation panel on the Desktop.
Within the applications drawer, use the search bar to search for “disks” and open its application by clicking on its icon.
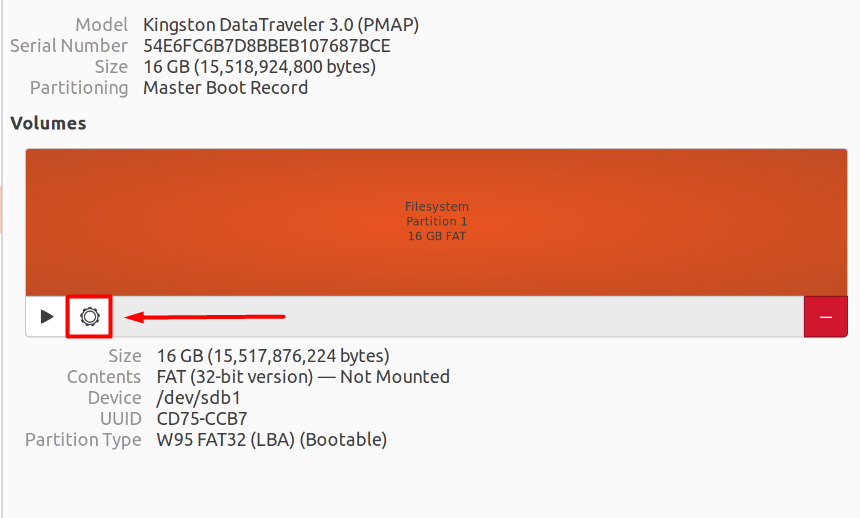
Once inside the “Disks” application, find your Pen drive or external storage device from the life-side panel and click on its name to view its details in the explorer tab.
After that, find and click on the tiny “Gear-box” icon from the explorer tab to open up the settings for the connected pen drive.
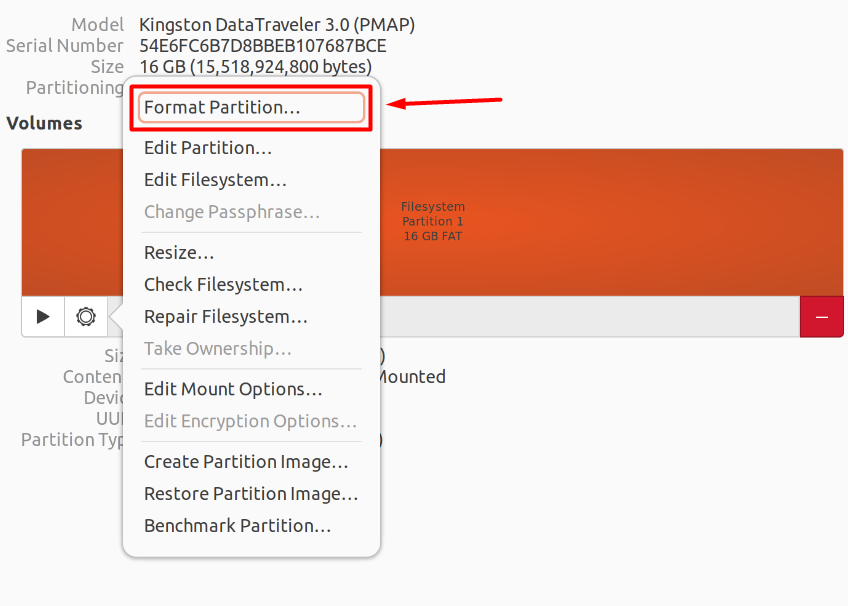
From the options that pop up after clicking the gear icon, choose “Format Partition…” to open up the format wizard.
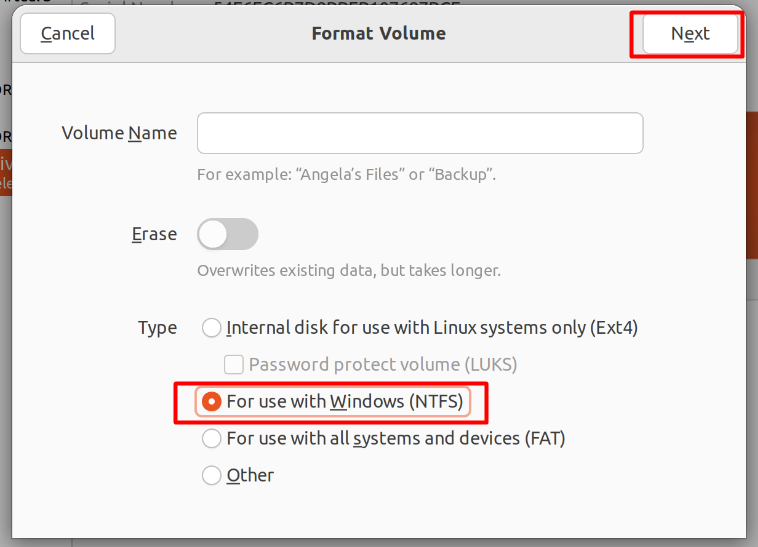
Inside the Format Partition Wizard, give your external storage device a label (optional) and make sure to choose the “Type” as “NTFS” or “EXT4” and then click on the “Next” Button.
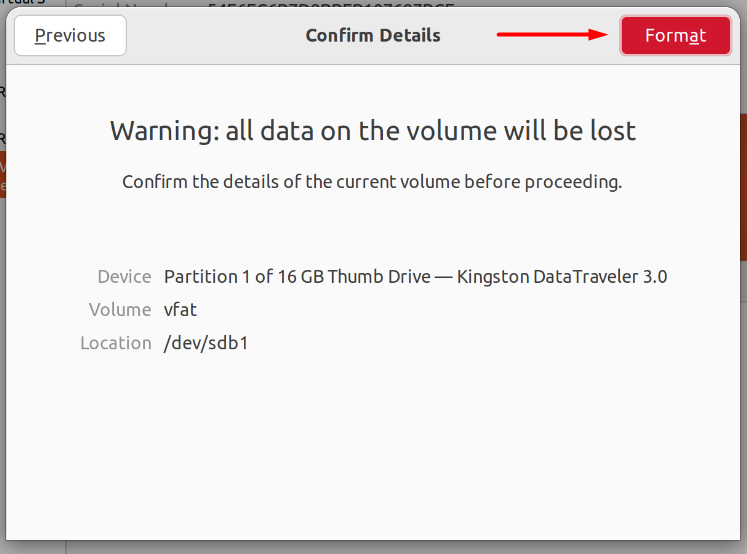
On the next page, you will be shown a confirmation message. Press the “Format” button to format the device and change its Format type.
Once done, you can retry the copy process into the external storage device and copy the files without encountering the “Files too large” error.
Use Correct Path While Copying File
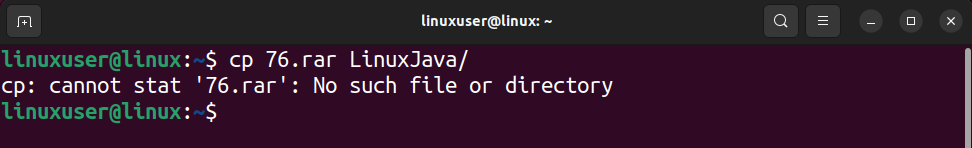
If you are trying to copy files from one location to another but encounter the error “no such file or directory,” you must use the correct paths and ensure no typing error.
To demonstrate this, assume you want to copy the file “76.rar” into the folder named “LinuxJava.” Both the file and the folder are placed on the Desktop. You will get the following error if you open up a terminal and run the copy command without changing the working directory.
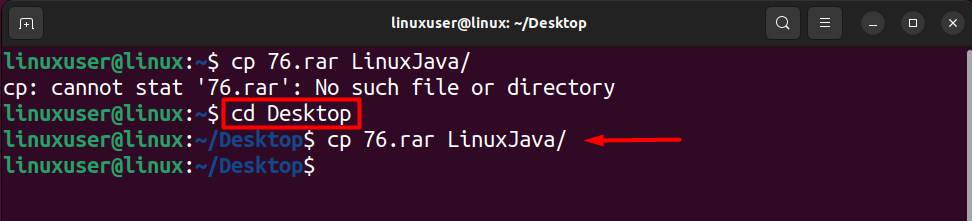
First, observe which file gives the error. The file to be copied or the destination to be copied in. In the current case, the file that needs to be copied gives the error. After that, ensure two things: there are no spelling mistakes in the names of the files, and the present working directory is the same as the directory that contains the file.
Since the file is placed on the Desktop, you must also change the pwd to Desktop by running the following command.
cd Desktop
Once that is done, rerun the copy command, which will work without encountering any errors.
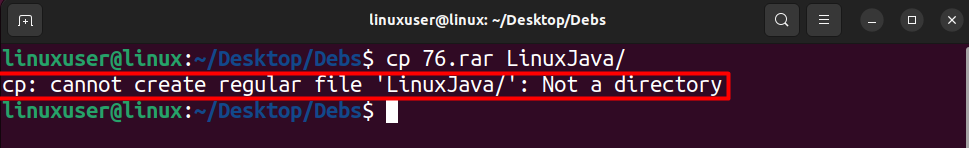
However, if you are already inside the directory containing the file and the destination directory, it gives the error.
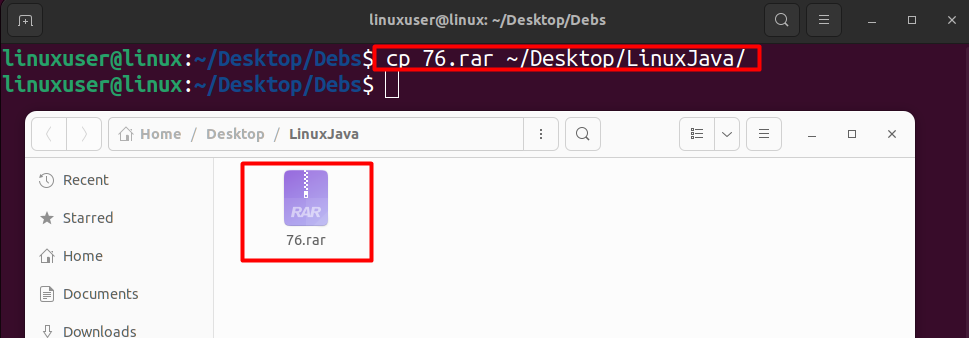
First, check if there is a type in the directory name. Otherwise, you will need to provide the complete path of the destination directory if it is not in the same PWD. If the destination folder is not the Desktop and the file to be copied is in the PWD, then you will have to run the following command template.
cp 76.rar ~/Desktop/LinuxJava/
Once you do that, you will observe that the file has been copied successfully without encountering any errors.
That sums up this guide!
Conclusion
If you encounter the “permission denied” when copying a file from one location to another, you do not have ownership over the file or the directory in which the file is to be copied.
A quick fix is to use the “sudo” keyword at the start of the copy (cp) command or switch over to the root shell to execute the commands. However, be careful with this method, as the commands will be executed without prompts and can damage the system files.
Alternatively, if you encounter the error “read-only” while trying to copy files into a directory, use the “chmod” command to change the access rights of the directory. In case of a “files too large” error when copying the files into an external storage drive, ensure that the external drive uses the NTFS or ext4 file format.
Lastly, if you experience the “file not found” error, ensure that the PWD is the same as the file to be copied, the complete path of the destination directory is provided in the copy command, and there is no spelling mistake in the file’s names.
Check out More Linux Tutorials Here!
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
Oldest