What Does sudo apt-get update Command do in Ubuntu?
Are you new to the Linux operating system and wondering what most commands do? Especially the command “sudo apt-get update” is used in almost every tutorial you find online. If that is the case, you are in the right place.
This guide will teach you the purpose and use of the sudo apt-get update command in Ubuntu/Linux. So, let’s get started!
The Purpose of the apt-get update Command
The “apt-get update” command is used to check all entries of the “apt” packages list to see if any update is available for any package from all of the sources that are added to the “source” list. However, the prefix sudo is used to utilize administrator rights while trying to execute this command.
However, unlike other operating systems, “update” doesn’t mean it will start updating the packages to their latest version. It will only update the list, which contains information about the version of the packages, their dependencies, their work environment, and more.
How to use the sudo apt-get update Command in Ubuntu?
To run this command or to update the packages list, simply open up a terminal in Ubuntu by right-clicking:
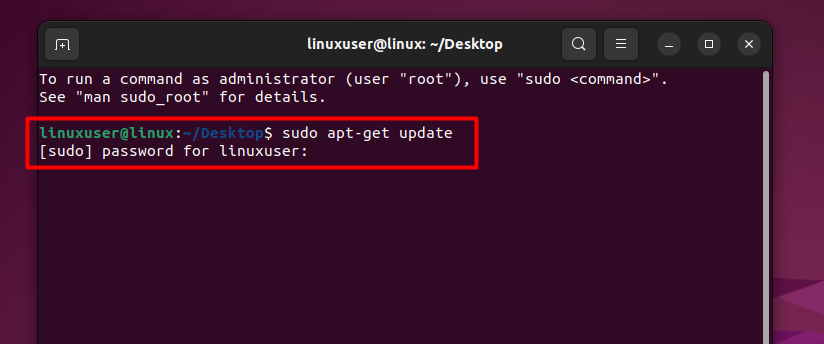
After that, type the command in the terminal and hit the enter key, and the terminal will show you the following prompt:
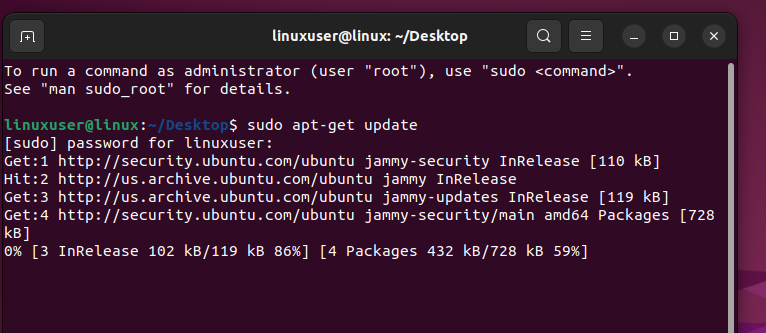
As you can see, it is asking for the root user’s password. Provide that and hit the “Enter” key again to start the updating process:
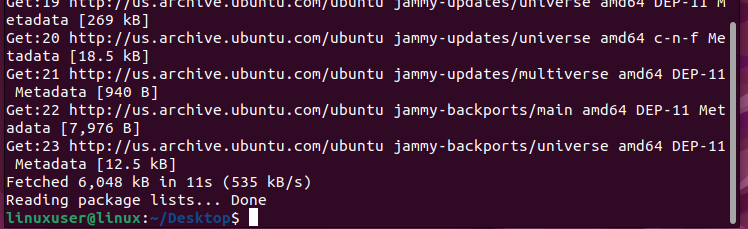
Running this command for the first time on your Ubuntu/Linux Installation might take a little while. However, once it is done, you will see the following output on the terminal:
This means that the apt packages list is fully up-to-date. However, let’s address more information regarding the sudo apt-get update command.
What is “apt” in the sudo apt-get Command?
Most new beginners are confused about this command because the word “apt” is often used in Ubuntu commands. Well, to put it short, apt is a package manager in Ubuntu. That is why the apt package list keeps the information about all the packages so that the apt tool can perform actions on those packages according to the user’s requirements.
Where are the Sources for Packages Defined?
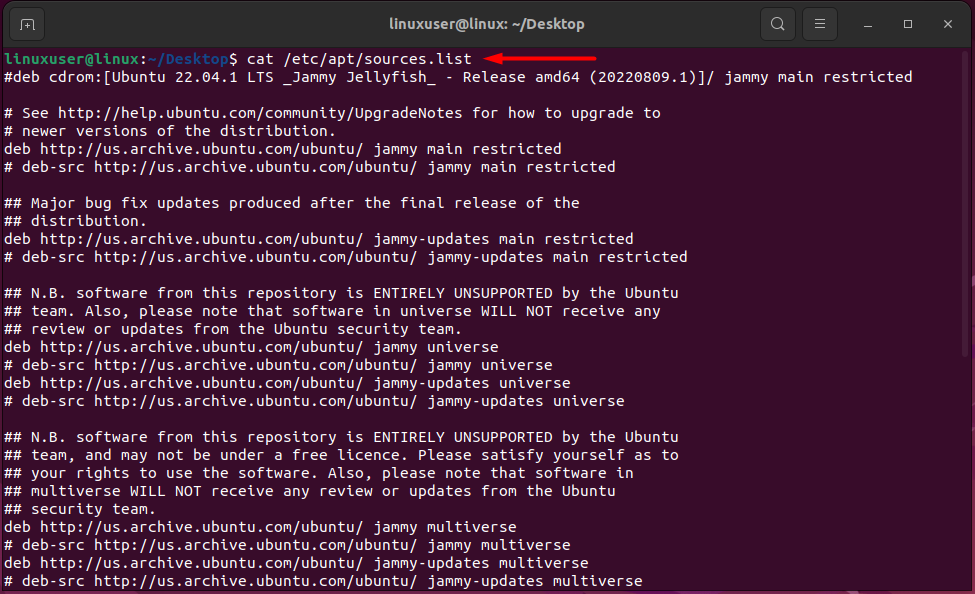
The sources are configured in the “/etc/apt/sources.list” which is placed in the “/etc/apt/sources.list.d” directory.
To view the sources file in your Ubuntu Installation, you can run the following command in the terminal:
cat /etc/apt/sources.list
Running this command will show the following output on the terminal:
These are all of the sources that will be checked for any new version of installed packages. But you might have seen the “apt update” command instead of the “apt-get” update. Let’s talk about their difference.
What is the difference between apt-get update and apt update?
There is practically no difference between the main purpose of the “apt-get update” command and the “apt update” command. The only difference is the information displayed on the terminal after updating the apt packages list.
The “apt update” command shows the total number of packages that can be upgraded and the command to execute if the user wishes to upgrade those packages. On the other hand, the “apt-get update” command doesn’t show any additional information. Rather it simply displayed that the apt packages list had been successfully updated.
Now, you are even familiar with the almost identical commands that confuse the minds of many new Ubuntu Users. However, there is still an unattended question: When should you run the apt-get update command?
When to run the “sudo apt-get update” Command?
The apt update command should be run periodically in a Linux-based operating system that uses the Advanced Package Tool (APT) for package management. This command retrieves the latest package information from the configured repositories and updates the local cache, allowing the system to know about the latest software packages and their dependencies.”
The apt update command is essential before installing new software or updating existing packages. This ensures that the system has the latest information about available packages and their dependencies, which helps prevent any issues arising from outdated package information.
It is recommended to run an “apt update” at least once a day to ensure that the system stays up to date with the latest software packages and security updates. However, depending on the use case and the frequency of software updates in the configured repositories, it may be necessary to run the command more frequently.
Now you know what this command does, but how do you update a package to a new version in Ubuntu?
How to Update a Package in Ubuntu?
To update a package in Ubuntu, you must utilize the “upgrade” command. However, the upgrade command is used after updating the apt packages list. To upgrade, type the following command in the terminal:
sudo apt-get upgrade
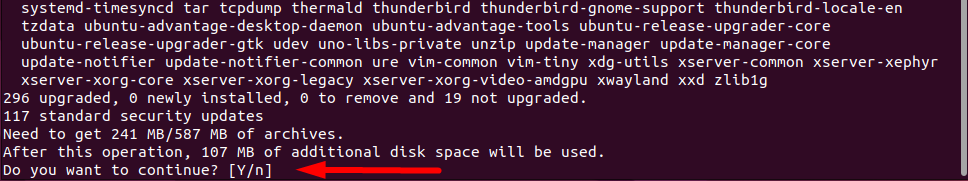
The terminal will ask you for the root pass. After you have provided the password, it will show the following output:
As you can see in the above output image, the system is asking for confirmation to download and install packages. Therefore, type “Y” and press the “Enter” key to start the upgradation process.
Dracula VPS Hosting Service
Dracula Servers offers high-performance server hosting at entry-level prices. The plans include Linux VPS, Sneaker Servers, Dedicated Servers & turnkey solutions. If you’re looking for quality self-managed servers with high amounts of RAM and storage, look no further.
Check the plans for yourself by clicking Here!
How to fix “Could not get lock /var/lib/dpkg/lock-frontend”?
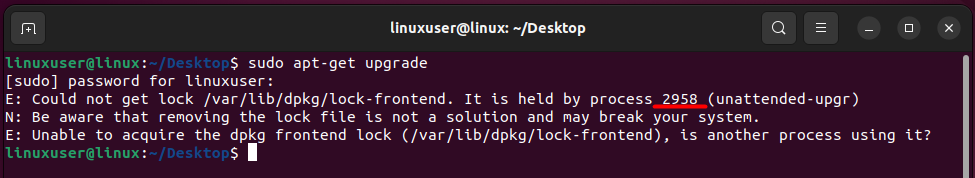
Often, when a user is trying to upgrade the packages on his Ubuntu Installation, he is met with the following error. This error simply means that some other process uses the system to perform an update. And the program that is using the system is also mentioned in the error statement shown:
To fix this error, simply use the “kill -9” command followed by the process ID mentioned in the error statement. For the above example, the kill command will be as follows:
Once that is done, run the command that caused this error, and it will execute without interruptions.
Is it safe to Interrupt the “apt update” Command?
Interrupting the apt update command is generally safe, as it has no adverse effects on the system. This command aims to update the package index, which is a local cache of available packages and their versions in the repositories that have been configured. It is important to note that this command does not modify or install any packages on the system.
Although interrupting the apt update command may result in an incomplete or outdated package index, this can be easily fixed by running the command again later. It is quite common to interrupt an apt update command, especially if it takes a long time to complete or if there is a network interruption or other issue.
However, it is worth noting that interrupting an apt update command may sometimes leave the package index in an inconsistent state, which can cause issues when installing or upgrading packages on the system. Therefore, ensuring that the apt update command completes successfully before performing any package installations or upgrades is recommended.
That also sums up this post!
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
Oldest